Masehi-Hijriyah
Hari Ini
📅
Memuat...
🌙
Memuat...
*Berdasarkan kalender Umm al-Qura
Popular Posts
-
Freepik.com Holistic care (Perawatan Holistik) adalah pendekatan dalam perawatan yang memandang individu secara menyeluruh, meliputi aspe...
-
Latar Belakang Kehidupan dan Prestasi yang Diraih Betty Neuman lahir pada 11 September 1924 di wilayah tenggara Ohio, Amerika Serikat. Ia ...
-
Lamtoro atau petai cina (nama ilmiah: Leucaena leucocephala ) adalah tanaman polong-polongan yang berasal dari Amerika Tengah dan Meksik...
-
www.freepik.com Rencana Pembelajaran Semester (RPS) Mata Kuliah Biostatistik Kontrak Pembelajaran Mata Kuliah Biostatistik (Masih dibu...
-
Pernahkah Anda merenungkan sebuah paradoks di mana rasa lapar justru menjadi "bahan bakar" utama bagi kejernihan pikiran? Selama...
Blog Archive
-
▼
2022
(42)
-
▼
March
(15)
- The Theory of Cultural Care Diversity and Universa...
- Bahan Ajar KDK: Neuman System Model (NSM)
- Bahan Ajar KDK: Nurse-Patient Relation Theory
- Tindakan Keperawatan: Pemberian Enema/Klisma
- Bahan Ajar KDK: Orem's Self Care Deficit Nursing T...
- Bahan Ajar KDK: King's Theory of Goal Attainment
- Hemodialisa
- Bahan Ajar KMB 2: Asuhan Keperawatan Perioperatif
- Bladder Training
- Perawatan Kateter Urin
- Bahan Penyuluhan Pengabmas: P3K Bagi Orang Awam Ke...
- Bahan Ajar KDK: Roy Adaptation Model (RAM)
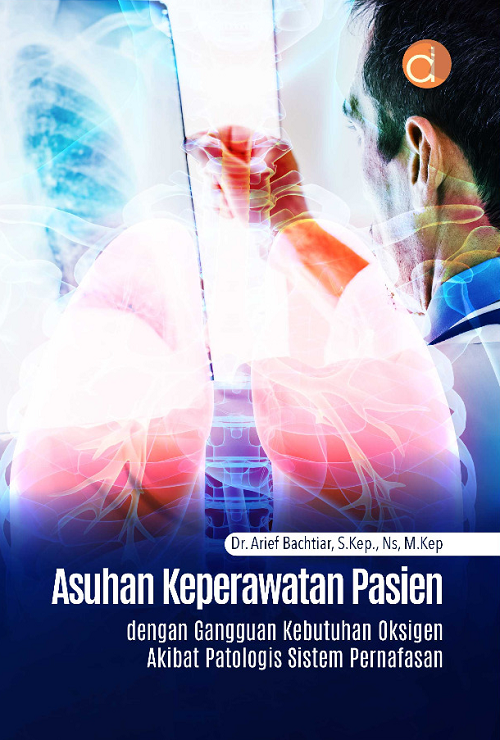
- Bahan Ajar KMB 1: Askep Gangguan Kebutuhan Cairan
- Prosedur: Digital Disimpaction (Evakuasi Feses Sec...
- Bahan Ajar KMB 1: Askep Gangguan Kebutuhan Eliminasi
-
▼
March
(15)
Total Pageviews
Followers
Website
Abi. Powered by Blogger.






Leave a Comment